Newton’s laws
1st Law
A body moves with a constant unless acted by a force. The statement gives us a definition of an inertial frame, where 1st law holds.
2nd Law
Newton’s second law is not just a Force definition, but it has some real-world implications, as shown in the textbook in contrast to a made-up definition. By the way, argue why can’t be true?
3rd Law
Interestingly, the third law is equivalent to the conservation of momentum! If we have particles that interact with each other only:
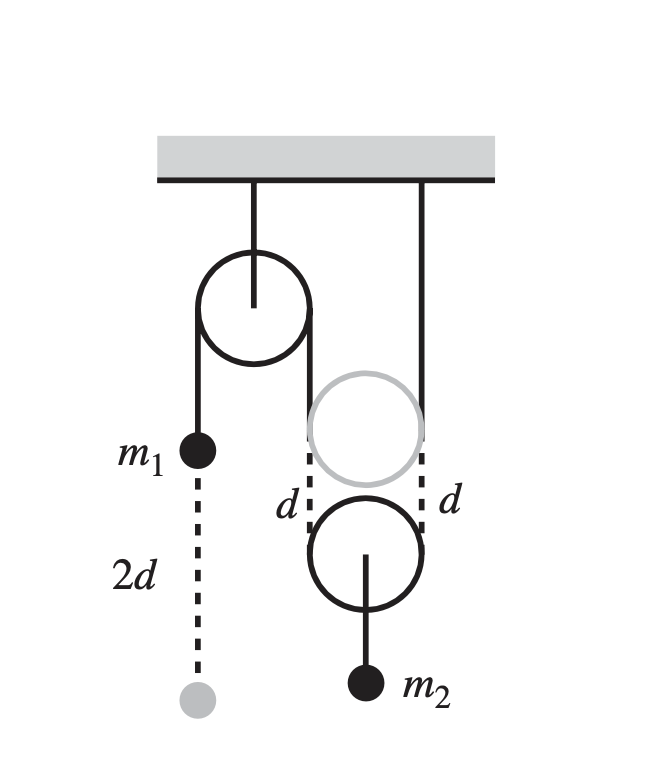
Atwood’s machine
Problems on this topic rely on just writing down equation and using conservation of string fact. Recall the simplest case where
Fall with a drag
The differential equation is . From this, we can get . The limiting case for large suggests that an object reaches a terminal velocity, . In free fall, we discover that all objects fall at the same rate independent of their mass. However, if we consider drag, then plays a role! But we don’t notice it because in a thin medium drag is a minor effect. Btw, solving the equation and deriving is not hard.
Motion
Fall with a drag
The differential equation is . From this, we can get . The limiting case for large suggests that an object reaches a terminal velocity, . In free fall, we discover that all objects fall at the same rate independent of their mass. However, if we consider drag, then plays a role! But we don’t notice it because in a thin medium drag is a minor effect. Btw, solving the equation and deriving is not hard.
Projectile
Without a drag, our two equations of motion are “decoupled”: From this you can derive two sets of equations for velocity and position. An interesting problem arises when the ground is inclined. Can you recall the key idea to solve it?
Polar coordinates
It might be a good question to ask how F=ma looks in polar coordinates. The derivation is quite tedious, but you should have a sketch in your mind. You start by defining and taking derivatives. Remember that you need to differentiate . The result is
Recall what each term means.
Problems to solve in Newton’s law Problems.